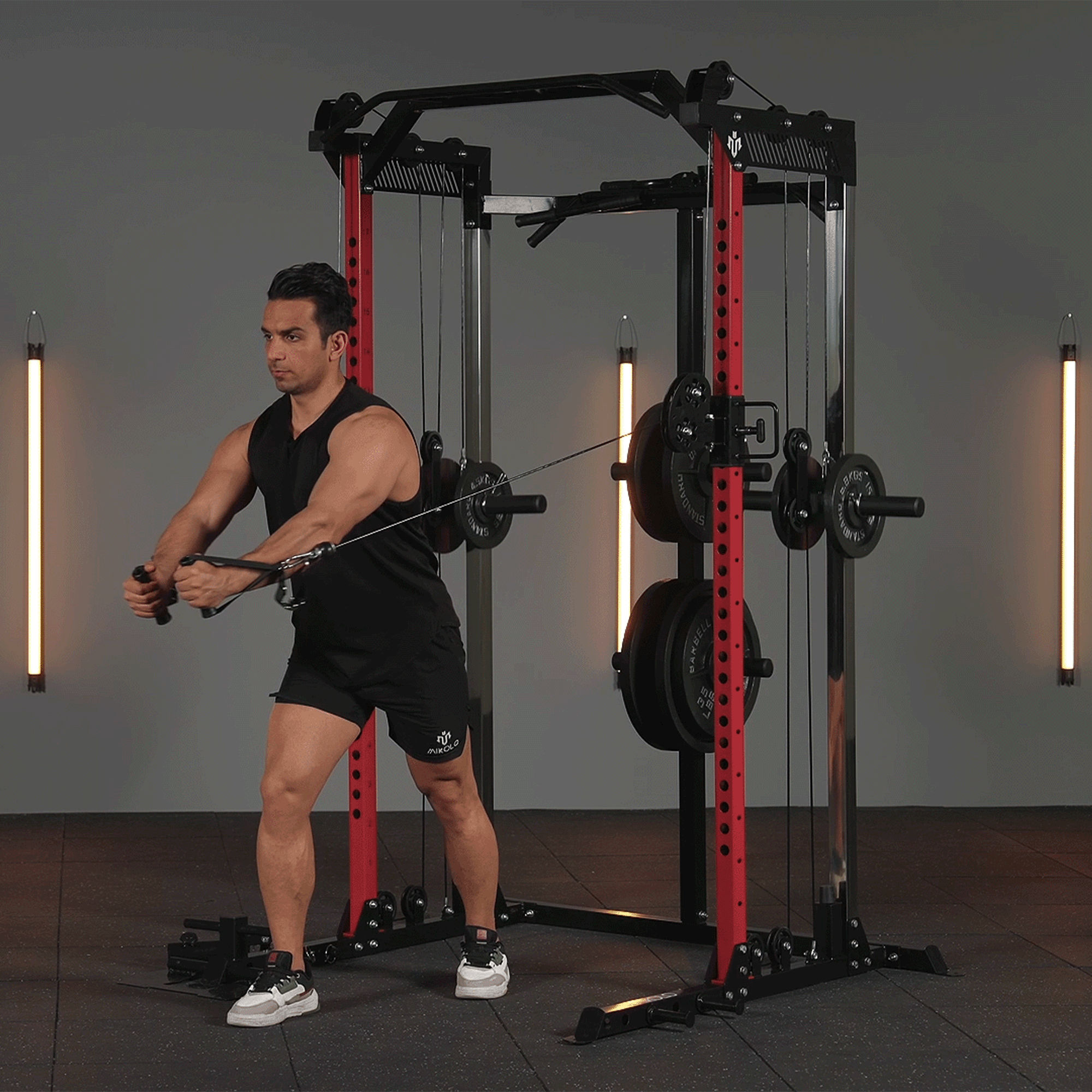
Low rows are one of the best exercises for building a strong and well-defined back. Whether you are an athlete, bodybuilder, or fitness enthusiast, incorporating low rows into your workout routine can significantly enhance your upper-body strength and posture.
This exercise primarily targets the low row muscles, including the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and traps. In this guide, we’ll cover everything from what is a low row to the best techniques for maximizing gains.
What is a Low Row?
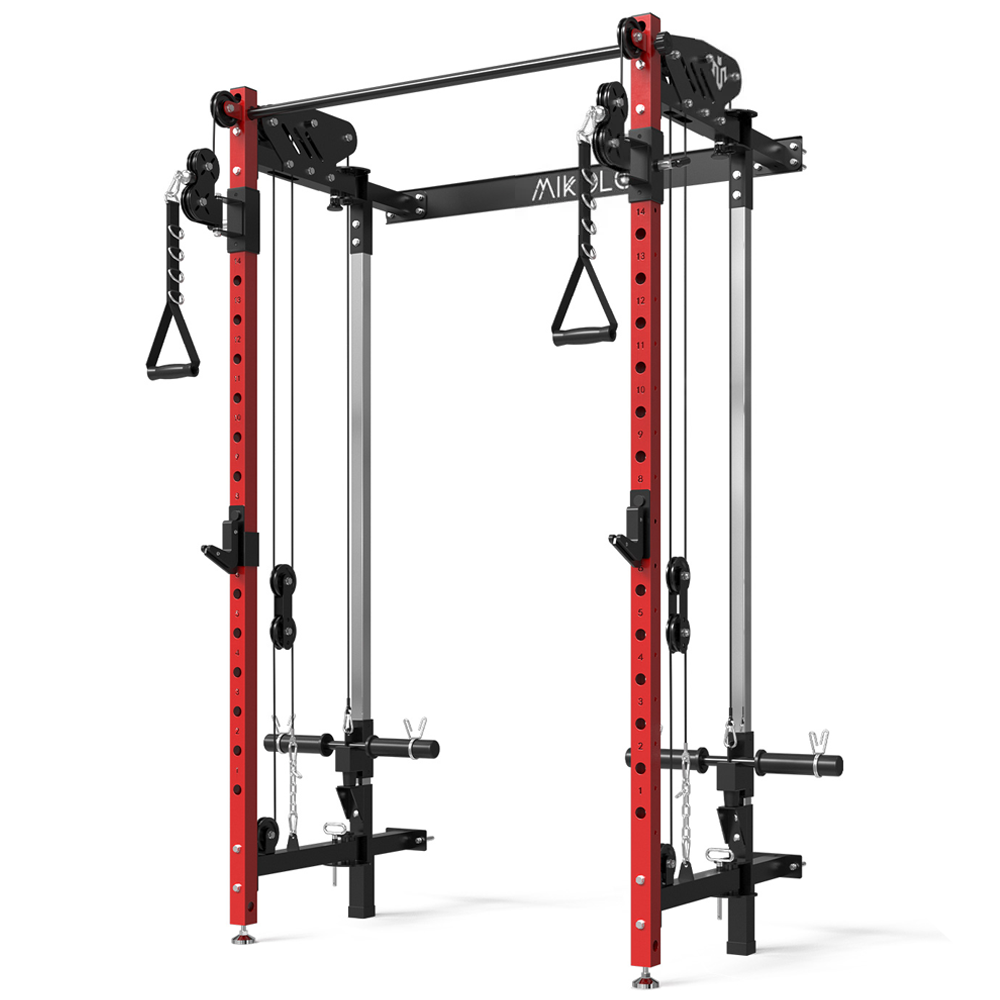
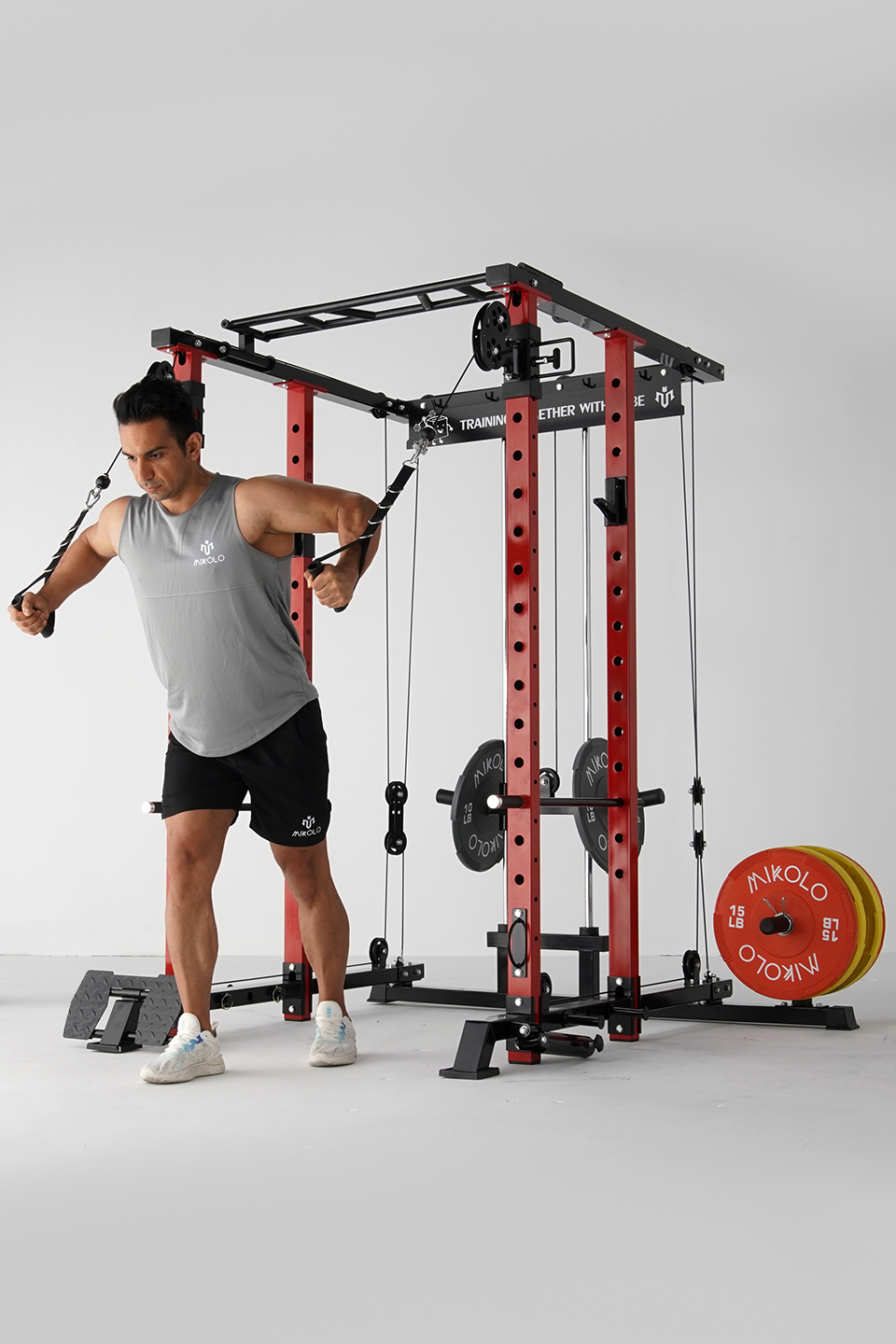
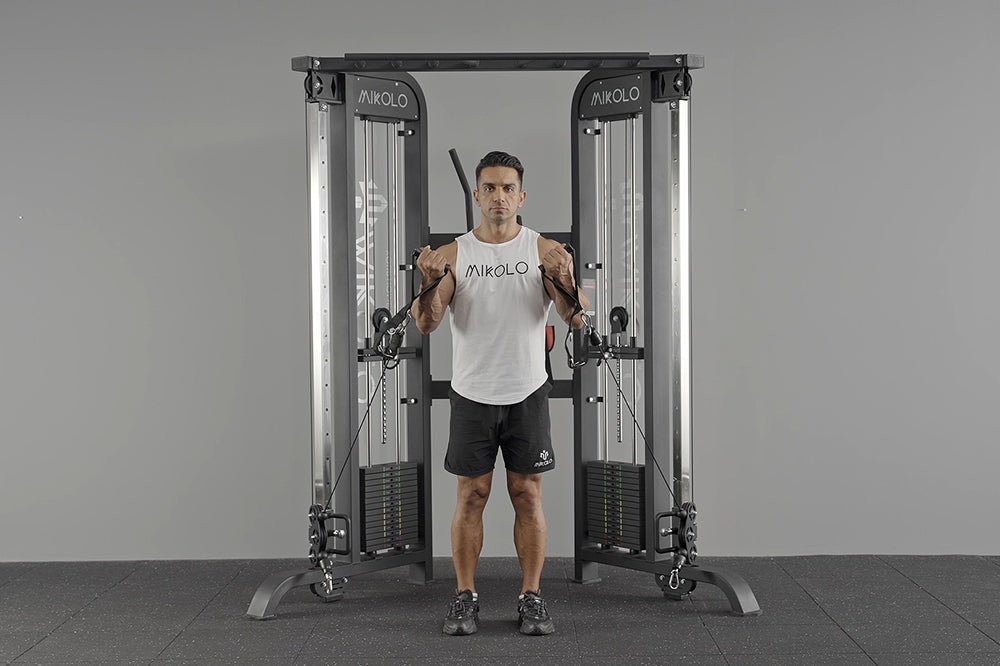
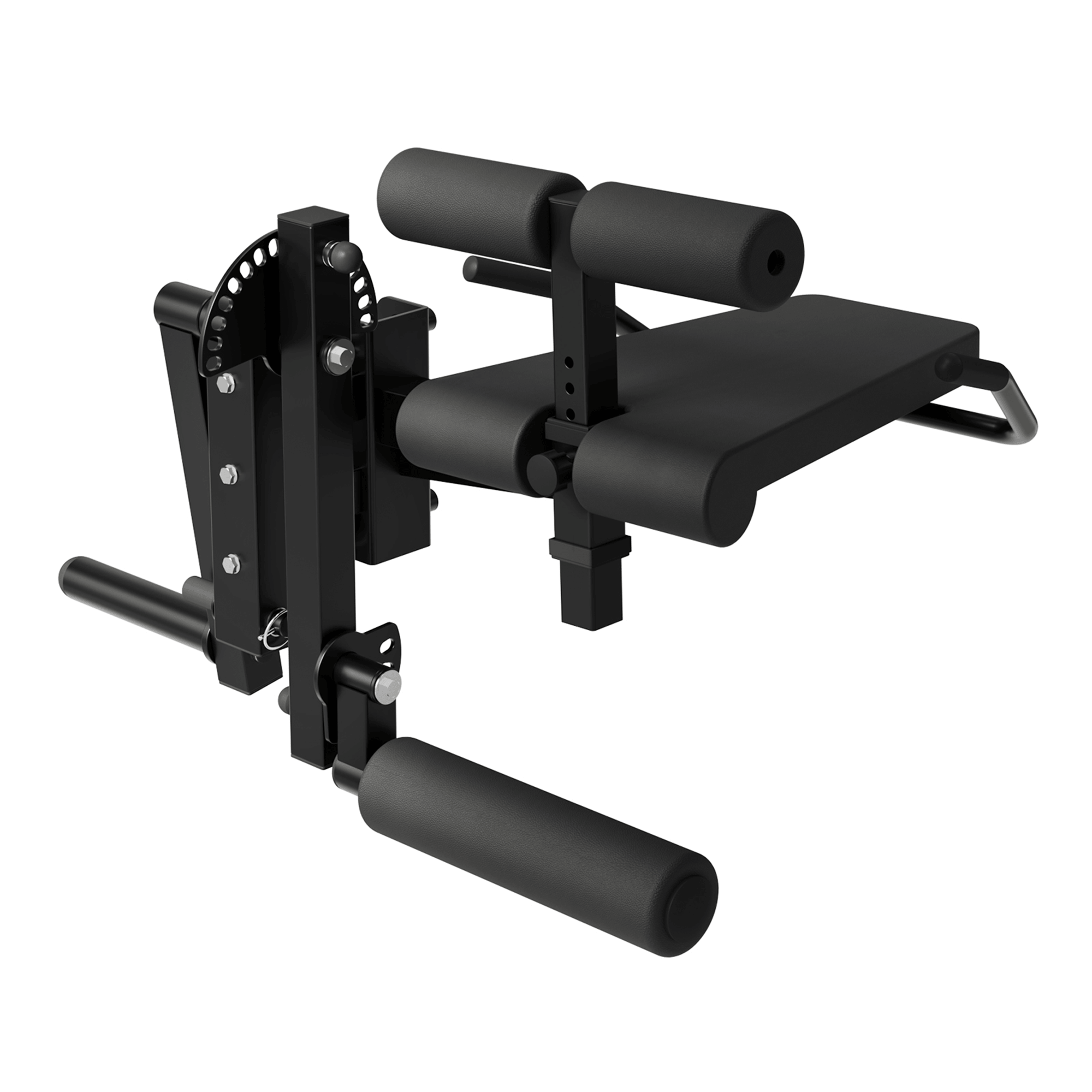
A low row is a strength-training exercise that focuses on the back muscles. It is typically performed using a cable row machine, a resistance band, or a barbell. The movement involves pulling a weight towards your torso while maintaining a strong posture.
How It Works:
- Sit on a low row machine or bench with your feet flat.
- Grab the handle with both hands, keeping your back straight.
- Pull the handle toward your body while squeezing your shoulder blades.
- Slowly return to the starting position.
Low Row Muscles Worked
Low rows engage multiple muscle groups, including:
- Latissimus Dorsi (Lats): The primary muscle responsible for pulling movements.
- Rhomboids: Located between the shoulder blades, these help in scapular retraction.
- Trapezius (Traps): Assists in shoulder stability and movement.
- Biceps Brachii: Involved in the pulling motion.
- Erector Spinae: Helps maintain spinal stability during the movement.
Benefits of Low Rows
- Strengthens the Back: Builds a powerful, well-defined back.
- Improves Posture: Encourages proper spinal alignment.
- Enhances Pulling Strength: Useful for sports like rowing and climbing.
- Reduces Injury Risk: Strengthens muscles that support the spine.
- Develops Muscle Definition: Great for building a thicker back.
How to Perform a Low Row Correctly
- Set Up the Machine: Adjust the seat and footrest.
- Grip the Handle: Use an overhand or neutral grip.
- Pull Towards You: Keep your chest up and squeeze your shoulder blades.
- Control the Eccentric Phase: Slowly extend your arms back to the start.
Pro Tip: Avoid rounding your back to prevent strain.
Types of Low Row Exercises
- Seated Cable Low Row
- Bent-Over Barbell Row
- Dumbbell Low Row
- Resistance Band Low Row
- Smith Machine Low Row
Each variation offers unique benefits depending on your fitness level and goals.
Seated Low Row vs. Bent-Over Row: Key Differences
| Feature | Seated Low Row | Bent-Over Row |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Cable Machine | Barbell/Dumbbells |
| Posture | Seated, back supported | Bent-over, core engaged |
| Muscle Focus | More on middle back | More on lower back |
| Difficulty Level | Beginner-friendly | Requires more stability |
Common Mistakes in Low Rows and How to Fix Them
- Rounding the Back: Keep your spine neutral.
- Using Too Much Weight: Start light to master form.
- Not Squeezing the Shoulder Blades: Engage the back fully.
- Jerky Movements: Use a slow, controlled motion.
Low Row Machine vs. Free Weights: Which is Better?
- Machine Rows: Great for beginners, safer for joints.
- Free Weights: Builds stability and engages more muscles.
For a balanced workout, incorporating both can be beneficial.
Best Low Row Variations for Maximum Gains
- Close-Grip Low Row: Focuses on the middle back.
- Wide-Grip Low Row: Targets the lats more.
- Single-Arm Low Row: Improves muscle imbalances.
Low Row for Beginners: Step-by-Step Guide
- Start with a lightweight.
- Focus on form over weight.
- Perform 8–12 reps per set.
- Keep the movement controlled and steady.
Low Row Workout Plan for Strength and Hypertrophy
| Day | Exercise | Sets x Reps |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Seated Cable Row | 4 x 12 |
| Wednesday | Dumbbell Low Row | 3 x 10 |
| Friday | Barbell Bent-Over Row | 4 x 8 |
Tips to Improve Your Low Row Performance
- Use a full range of motion.
- Incorporate different grips.
- Progressively overload (increase weight gradually).
- Maintain proper posture.
Frequently Asked Questions About Low Rows
1. What muscles do low rows work?
Low rows primarily target the lats, rhomboids, traps, and biceps.
2. Is a low row better than a pull-up?
Low rows are easier for beginners, while pull-ups engage more upper-body muscles. Both are excellent for back strength.
3. Can low rows help with posture?
Yes! They strengthen the upper and mid-back muscles, improving posture.
4. How many sets and reps should I do?
For strength: 4–6 reps per set. For muscle growth: 8–12 reps per set.
5. Should I use a machine or free weights for low rows?
Beginners should start with a machine, while advanced lifters can use free weights for added difficulty.
6. How often should I do low rows?
2–3 times per week for best results.
Conclusion: Why Low Rows Should Be in Your Routine
Low rows are a must-have for anyone looking to build a strong, muscular back. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced lifter, incorporating low row exercises into your routine will enhance strength, posture, and overall fitness.
Start with proper form, progress gradually, and reap the benefits of a well-developed back!









































Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.